Understanding VBA in Excel helps you to automate your work, create macros, and improve your data handling abilities. This guide offers practical examples and highlights best practices to get you started.
💡 Ready to test your Excel knowledge?
🚀 Don't Miss This Important Resource!
Explore Our Advance Xcel Tools Free !VBA stands for Visual Basic Analysis. Excel VBA is Microsoft’s programming language for Office programs like MS-Excel, MS-Word, and MS-Access. Most VBA coders use macros. VBA in Excel is a language that allows users to automate difficult processes and improve Excel’s functionality far beyond its normal features.
In this article, I’ll cover core and advanced VBA concepts. However, if you’re new to Excel, begin with Excel Fundamentals to develop a solid foundation before advancing to VBA.
What is VBA in Excel?
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a human-readable and editable programming language that is generated when recording a macro. Currently, it is widely used together with other Microsoft Office applications such as MS Word, MS Excel, and MS Access.
Important VBA Excel Terms
Before working with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), you must learn its keywords and concepts. Here is a list of some of the most common Excel VBA terms:
- Modules are containers for VBA code that store procedures and functions.
- Objects are the building blocks of VBA. They reflect elements like workbooks, worksheets, and cells.
- Procedures are the blocks of code that perform specific jobs, often categorized as sub-procedures or functions.
- Statements are the instructions within a procedure that tell Excel (or Word or Access) what steps to perform.
- Variables store info that can be used and manipulated within your code.
- Logical operators compare values and make choices based on the results. They include operators like And, Or, and Not.
ALSO READ: How to Change HORIZONTAL Data to VERTICAL in Excel
Getting Started with VBA in Excel
To begin using VBA, you’ll need to access the VBA editor. This is where you’ll write and edit your Excel VBA code. Let’s walk through how to get there:
Enable Developer Option in Excel
By default, the Developer tab is hidden in Excel. To enable it:
Step 1: Right-click on the ribbon and click on the Customize the Ribbon option.
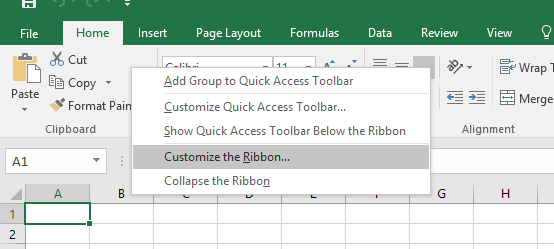
Step 2: Then Go to Customize the Ribbon and select the Developer checkbox.
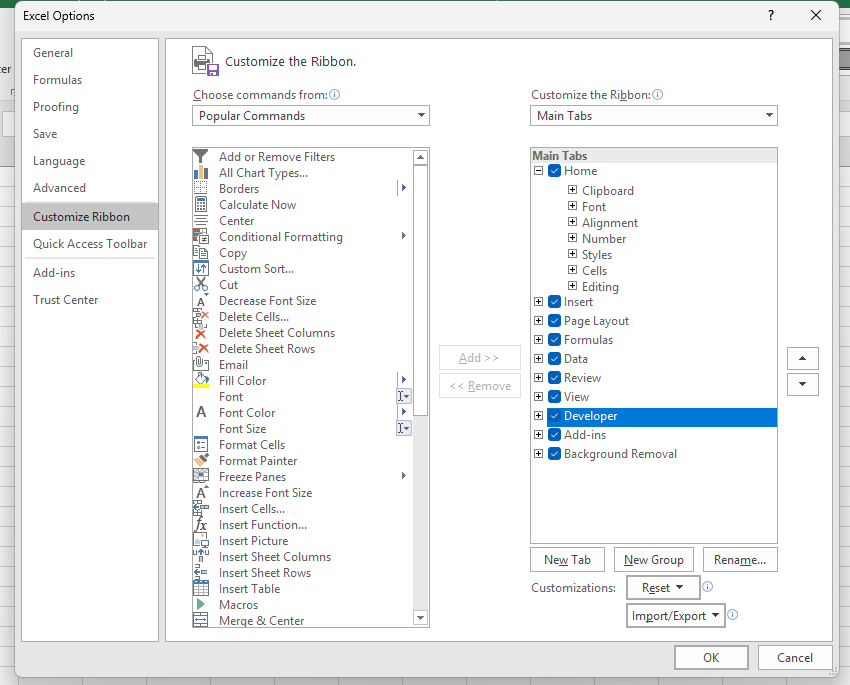
The Developer tab provides access to VBA tools, macros, and the Visual Basic editor.
How to Open VBA in Excel?
There are two simple ways to open the VBA Editor in Excel, where you can edit and write code.
Step 1: You can simply Go to Developer and then select Visual Basic.
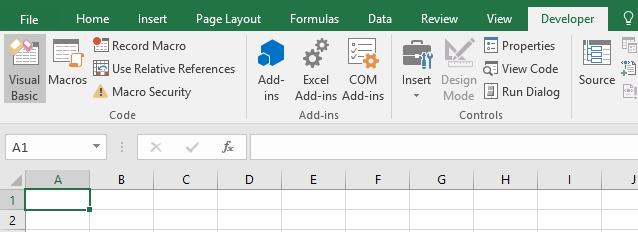
Step 2: Or, you can just press Alt + F11, and the VBA editor will open.
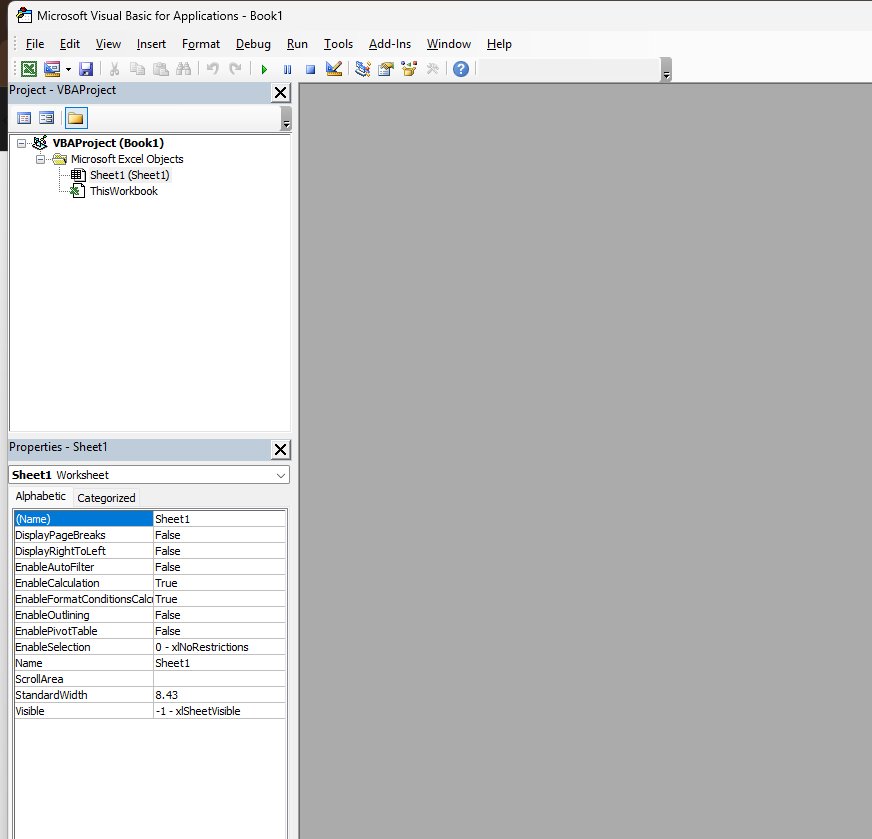
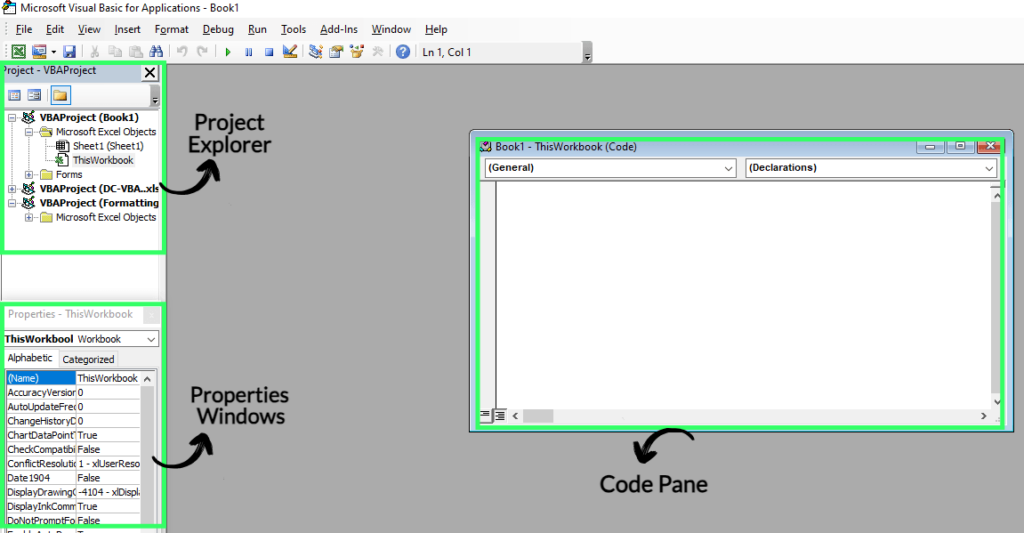
Exploring the VBA Interface
The VBA editor might initially seem confusing, but it’s easy to use. Let’s understand its few important areas:
- The Code Pane is where you write and edit your VBA code.
- Project Explorer shows a hierarchical view of the projects and modules in your workbook.
- The Properties window shows properties for selected objects to customize their settings.
Writing VBA Code in Excel
Now that you’re comfortable with the VBA editor, it’s time to start writing some code. VBA code is made up of various parts, such as sub procedures and functions, which are sets of instructions that tell Excel what to do. Don’t worry if you’ve never programmed before; I’ll guide you through it step by step.
Writing a VBA subroutine
To write a macro, you must first create a macro environment. To do so, take the following steps:
- Within the VBA editor, select Insert > Module. A new module will be created with the default name Module1.
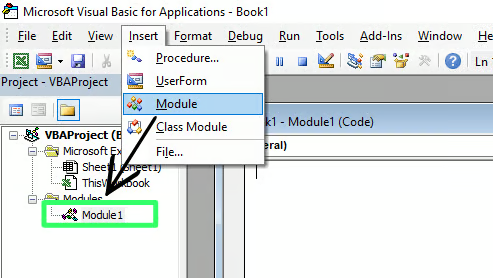
- You can change the module name in the Properties pane.
Now that you’ve learned how to set up the environment for creating a macro, let’s collaborate and create our first macro to display a message. When you create a module, the code window automatically opens. If it doesn’t work for you, right-click the module you created and select View Code. The code window will appear, allowing you to write your macros.
Now I will guide you on how to create your first macro to display the message “Hello, World!” To do so, write the following code in the code pane:
Sub ShowMessage()
MsgBox "Hello, World!"
End Sub How It Works:
- Sub starts the macro.
- MsgBox shows a message.
- End Sub stops the macro.
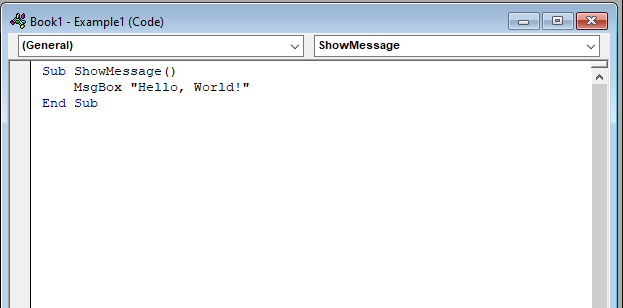
Now it’s time to run the code. Use the shortcut key F5. If you wish to do it manually, click on the Developer tab and select Macros. Hit the run button.
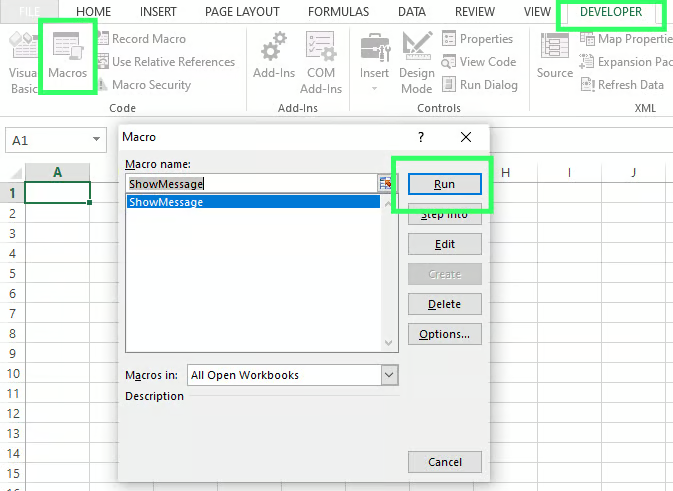
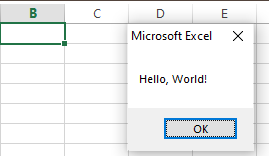
The message box will now appear on your Excel sheet.
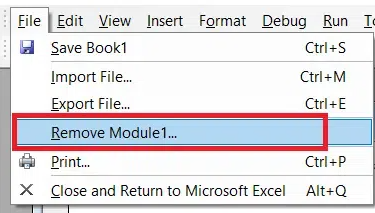
How to Delete a Module in VBA Excel
Step 1: Right-click on the left pane and select Remove Module.
To delete a module, right-click it in the left pane and select “Remove [module name].”
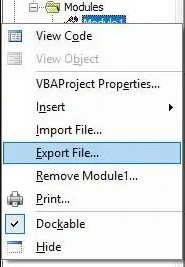
How to Export or Save a VBA module from Excel
If we want to save the module to the computer, right-click Module1 and select Export File.
Variables in VBA Excel
A variable is used to temporarily store data while the macro is running.
Imagine a variable to be a labeled box where a value can be stored.
Why Variables Are Important:
- Make coding flexible.
- Avoid repetition of values.
- Improve readability.
- Helps with calculations and logic.
Macro Comments In VBA
Comments are used to document program logic and user information, allowing other programmers to work on the same code in the future.
It contains information such as who created it, who modified it, and any logic that has been incorporated. The interpreter ignores comments during execution.
In VBA, comments are denoted using two methods.
Method 1: Any statement beginning with a single quote (‘) is treated as a comment. Here is an example.
' This Script is invoked after successful login
' Written by : TutorialsPoint
' Return Value : True / FalseMethod 2: Any statement that begins with the keyword “REM” is treated as a comment. Here is an example.
REM This Script is written to Validate the Entered Input
REM Modified by : Tutorials point/user2ALSO READ: How to Use VLOOKUP in Excel – A Step-by-Step Guide (With Examples)
Automating Some Common Excel Tasks with VBA
1. Automatically Formatting Data
This VBA macro formats header cells automatically.
Sub FormatHeaders()
Range("A1:D1").Font.Bold = True
Range("A1:D1").Interior.Color = RGB(200, 200, 200)
End SubInstead of manually changing fonts, colors, and borders, using VBA can format headers, highlight values, and organize sheets instantly, saving time, reducing errors, and improving the overall look of your data.
2. Looping Through Data
Looping through data in VBA Excel helps you to do the same action on multiple cells, rows, or columns automatically. Instead of handling each value manually, loops repeat instructions efficiently, making it easier to deal with large datasets, apply calculations, validate values, and clean or organize data fast and precisely.
Sub FillNumbers()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 10
Cells(i, 1).Value = i
Next i
End SubThis macro fills numbers 1 to 10 in column A.
3. Cleaning Data Automatically
Cleaning data automatically with VBA Excel helps remove blanks, fix formatting issues, and correct wrong entries. VBA can remove extra spaces, delete empty rows, normalize text, and handle errors across large datasets, making sure your data is accurate, well-organized, and ready for analysis or reporting.
Sub RemoveBlanks()
Columns("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Delete
End SubThis VBA macro removes blank cells from a column.
Final Thoughts
VBA Excel is a powerful but easy technique to automate tasks, reduce errors, and save valuable time. You don’t need to be a programmer to use it—just have a desire to learn and explore. By starting with simple macros and gradually exploring VBA features, you can transform Excel from a manual tool into an automated assistant.
Doesn’t matter if you’re a student or professional; learning VBA Excel can really improve how you deal with data. Begin small, practice regularly, and soon you’ll wonder how you ever handled Excel without automation.
💡 Ready to test your Excel knowledge?








